E-Sharp News
June 2021
Growth in the global orthopaedic devices market offers an attractive diversification strategy for the CNC tool cutting industry
The global impacts of COVID-19 are numerous and continue to affect people in ways that are unexpected. Stemming from this, the crisis response from the healthcare system in many countries was the necessary decision to stop all non-emergency procedures in order to direct resources towards tackling rising COVID cases. While the health system continues to face the challenges of the pandemic, many institutions are looking to ramp up elective surgery to address the backlog with careful planning.
In the UK, it is estimated that nearly 10 million people are waiting for surgical procedures, including joint replacement surgeries
[1]while one recent study in the US predicts that the post-pandemic backlog will exceed one million cases in orthopaedic surgery alone.
[2] Compounding these backlogs is the steady growth in orthopaedic surgery due to an aging population, with osteoarthritis being one of the most disabling diseases in developed countries.
The macro-economic challenges of the pandemic are also being experienced worldwide. For the tool grinding industry many traditional sectors are characterised by uncertainty. Now more than ever, diversification for tool and cutter grinding companies is a smart strategy. Diversification that follows opportunity is a proven method to protect and grow your business.
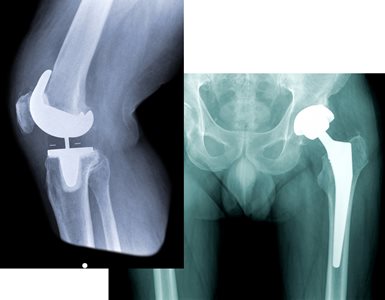 X-ray images of total knee and hip joint replacement
X-ray images of total knee and hip joint replacement
The global orthopaedic devices market size was valued at US$53.44 billion in 2019 and is expected to reach $68.51 billion by 2027 returning a CAGR of 6.6% between 2020 and 2027
[3], with joint reconstruction leading the market. For these reasons, the field of medical orthopaedic implant grinding is an attractive diversification strategy for the CNC tool cutting business. Joint reconstructive surgery is largely dominated by knee, hip and shoulder procedures, all of which involve orthopaedic implants and associated instruments that typically require grinding during the manufacturing process.
Grinding applications for the medical industry are characterised by high levels of customisation and complexity. Growth and technological advances in this area are opening doorways of opportunity to enter a lucrative market with strong historical and projected growth. Investment in the right machine tool coupled with industry-leading CAD/CAM software is crucial to remain competitive in this evolving market.
Grinding routines for orthopaedic applications, such as knee implants and bone rasps, are commonly produced using CAD/CAM packages such as Siemens PLM NX. Machine NC programs are generated using an NC Post-Processor for a specific machine target and are then used to manufacture the part. The post-processor forms an integral part of the integration between the CAD/CAM software and the machine. It is therefore important to ensure that this integration allows maximum flexibility during the design and production process.
 Femoral bone rasp used in hip joint replacement surgery
Femoral bone rasp used in hip joint replacement surgery
Satisfying geometry and surface finish requirements when grinding orthopaedic-grade alloys for medical implants can prove challenging. Integration between the CAD/CAM software and machine should ideally allow for easy and flexible programming of wheel-dressing routines as well as freedom to select various roughing and finishing grinding wheel geometries. A clear distinction should exist between the role of the CAD/CAM system and machine to avoid inefficiencies that arise when grinding-process changes require NC program regeneration from the CAD model.
The evolution and growth of the orthopaedics implant market fuels innovation into new products and manufacturing processes. As the market moves towards gender and patient-specific implants, manufacturers must ensure they employ the most cost-effective and viable manufacturing processes available. Software developments in the areas of CAD/CAM post-processing are providing significant productivity improvements and resulting in new CNC grinding solutions entering the market in recent years. This has led to a reduction of manufacturing lead times, allowing patient-specific implants to become a viable business with associated profit margins that custom implants command.
Integration between 5-axis CNC tool grinders and CAD/CAM software has provided an efficient solution to the challenges presented by the orthopedic implant market. Flexibility, productivity, automation, and integration with leading CAD/CAM systems are key competencies to identify when investigating potential solutions.
Mechanical meets medical: ANCA’s solution for orthopaedic implant grinding
With over 45 years of proven grinding solutions, ANCA have developed a solution for grinding CAD-designed parts from Siemens PLM NX CAD/CAM software by working with global leaders in the field of orthopedic implants as well as other industries.
By clearly defining the core responsibilities between Siemens NX and ANCA’s ToolRoom software, a post-processor has been developed that allows optimum integration between the two systems. The post-processor generates the grinding path information in a generic way so that all process-related tasks are delegated to the software.
Using a CAD model of a knee implant, the grinding path is defined within the Siemens PLX NX software
The logical separation of the grinding path generation with the manufacturing process introduces several advantages. The grinding path generation from the CAD/CAM system only needs to be generated once. This is then used on the machine where different diameter wheels can be used for roughing, finishing and sparkout operations, all using the same generated data. Wheel dressing seamlessly fits into this system without needing to return to the CAD/CAM system. The ANCA CNC’s 3D-CRC (cutter radius compensation) feature automatically calculates the modified grinding path, adjusting for the new wheel diameter on the fly. This allows parts to be ground using conventional or super-abrasive wheels using the same generated NC code.
This approach eliminates the need to regenerate the NC code from the CAD/CAM software when process parameters need adjusting, significantly optimizing the production. Adjustments and compensations can be made to the grinding path and wheels directly on the machine. NC code regeneration is required only when changes need to be made to the part’s geometry.
ANCA’s iGrind tool design software allows the generated NC code to be used in a dedicated iGrind operation, allowing all process parameters to be defined. This enables mixing of CAD generated operations with other standard grinding operations, allowing full flexibility in designing special parts. This also allows milling and drilling operations to be performed on one machine and in one set-up.
Seamless integration of the CAD generated geometry into ANCA’s iGrind software also means that the entire grinding sequence, including any additional operations, can be simulated in 3D using ANCA’s CIM3D software. Apart from offline geometry verification, potential collisions can be detected and cycle time estimation calculated.
ANCA’s TXcell provides both grinding and milling functions required to finish knee implants. With a polymer concrete base for superior vibration dampening, the TXcell features a 37KW (49HP) 10,000RPM spindle as well as a 3000RPM headstock dresser with additional provisions for a secondary rigidly mounted dresser with quick-change HSK arbours. The optional P-Axis provides CNC controlled tool support, including optional steady,
Arobotech or CNC force controlled tailstock. The TXcell has an optional wheel-pack exchanger model available with up to 24 wheel-packs. Automatic white-sticking is also available.
Automation for orthopedic implant applications typically benefit from the use of a Fanuc robot loader. Apart from providing automatic part loading capabilities, the robot can concurrently perform secondary tasks, such as polishing, within the loader envelope while the machine is grinding.
The best technology solution provides the flexibility to grind a wide range of orthopedic implants and standard cutting tools, ensuring maximum machine utilization and versatility. In a competitive market, investing in the right machine tool powered by leading software capabilities is a crucial step towards being successful, particularly in this dynamic field.
Republished with permission from APMEN: https://www.equipment-news.com/
21 May 2021